Chatea con Ava - Tu consultor de negocios IA
¡Hola, soy Ava, tu guía de IA para potenciar tu negocio!
Ya sea que dirijas una empresa o sueñes con iniciar una, estoy aquí para hacer realidad tu visión gracias a los freelancers que usan IA. Comparte los objetivos de tu negocio y juntos crearemos un proyecto en los que nuestros talentosos freelancers puedan ofertar. ¡Hagamos realidad tu visión!
Tengo un negocio
Estoy comenzando un negocio
Algo salió mal al enviar la conversación a tu correo electrónico. Por favor, intenta de nuevo más tarde.
Solo puedes guardar tu conversación una vez por hora. Por favor, intenta de nuevo más tarde.
Tu conversación es demasiado corta. Sigue chateando con Ava para poder guardar.
The best tools for code source control
If you don't have complete control over your code, things can get pretty ugly fast. Here are some of the best source control tools on the market.
28 jun 2019 • Lectura de 4 minutos
Actualizado el 23 ene 2020 por Adam S.

Content Manager at Freelancer.com
Falló el copiado al portapapeles. Intenta de nuevo después de ajustar tus permisos.
Copiado al portapapeles.
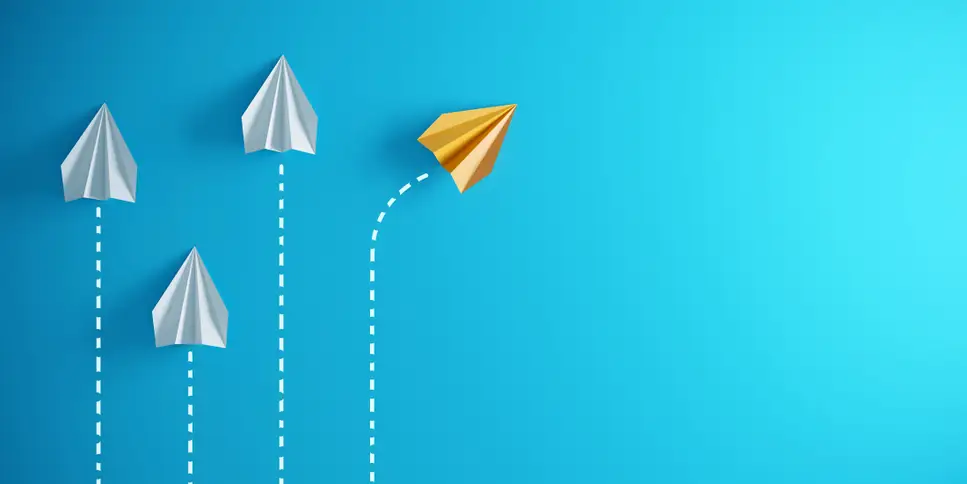

Version control is particularly important if you have multiple software developers on a project
Version control or source code control is essential to track the changes made to code. This is especially useful when problems pop up when there is more than one developer working on or changing source coding. Using version control allows developers to track back through the changes and revert to a previous version.
Source code management allows multiple developers working on a project to separate their work using branches that shows who makes what changes. You can view work history, use and manage code and revert to previous versions.
Software used to control versions saves changes in one place so if you make a mistake you can undo it or track back to find where another developer has made a mistake to resolve it.
There are many software version control tools available and you should choose the one that works best for you and your company.
Here are some of the best tools on the market.
Featured Work in Programming

WPF Agenda Scheduler
by amusto

WPF Hybrid App for Desktop & Tablet
by amusto

Bitrix24 Installation
by d1mf13

Ticketing System
by jameer8879
Git
Designed to operate on the Linus kernel, it does not have a central server so may not suit individual developers or small teams if using a non-repository computer. There are workarounds for this but it may slow you down.
Benefits of GIT include:
GitHub
It has Git’s functionality for source code management and distributed revision control but GitHub has a different set of features and functionalities.
GitHub benefits include:
GitLab
Benefits of GitLab include:
Beanstalk
It is customizable and has deployments in many environments so you can move code to individual or multiple servers at the same time.
Benefits of Beanstalk include:
Freelance Programming Experts


Proofreading
Excel
SQL
Powerpoint
Software Architecture


JavaScript
XML
.NET
Website Design
Photography

PHP
ASP
C Programming
Java
JSP

PHP
Python
Script Install
Windows Desktop
System Admin
Concurrent Versions Systems (CVS) is open source software first developed in 1986 and distributed under a GNU licence. It is one of the oldest, most mature source code management systems available. What sets CVS apart from other version control systems is its ability to run scripts when logging in. CVS run scripts allows developers working remotely to work as an integrated team and can also enforce site policies.
CVS benefits include:
Benefits of SVN include:
Bitbucket
Benefits of Bitbucket include:
Conclusion
These are among the best source control management systems for developers. But you have to choose the one that will work best for you. Consider use, purpose and affordability when making the best decision for your team.
Cuéntanos qué trabajo necesitas encargar
Ingresa el nombre de tu proyecto
Historias relacionadas
Habla con uno de nuestros Copilotos técnicos para que te ayude con tu proyecto
Artículos recomendados solo para ti

Brush up your entrepreneurial skill set with these free digital marketing courses
4 min read

Will your startup survive the AI revolution? We spoke to Greg Cross from Soul Machines to lean how to stay prepared.
4 min read

Learn the complete end-to-end process of building a successful website for your business in our comprehensive guide
19 min read

Great graphic design will solidify your brand identity and drive revenue. Find out how to hire a great designer and what you should expect to pay.
9 min read
¡Gracias! Te hemos enviado un enlace para reclamar tu crédito gratuito.
Algo salió mal al enviar tu correo electrónico. Por favor, intenta de nuevo.
Cargando visualización previa
Permiso concedido para Geolocalización.
Tu sesión de acceso ha expirado y has sido desconectado. Por favor, inica sesión nuevamente.




